Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
There have been so many great moments in the health technology sector, but this 3D-printed prosthetic is certainly among the most powerful. Brimming with brilliant genius of cutting-edge 3D printing with an enormous need for personalized health solutions, these gadgets bring hope and functionality to millions across the globe. The whole concept of 3D-printed prosthetics, in no way, denotes something for the future and opens up on how we perceive mobility, rehabilitation, and health.
The near future of healthcare is explored through 3D-printed prosthetics; its advantages, disadvantages, and what lies ahead for future developments.
Understanding 3D-Printed Prosthetics
3D-printed prosthetics are artificial limbs or devices manufactured using additive manufacturing technology. Unlike traditional prosthetics that generally depend on molds or standard designs, 3D-printed prosthetics have a level of customization according to each individual’s need.
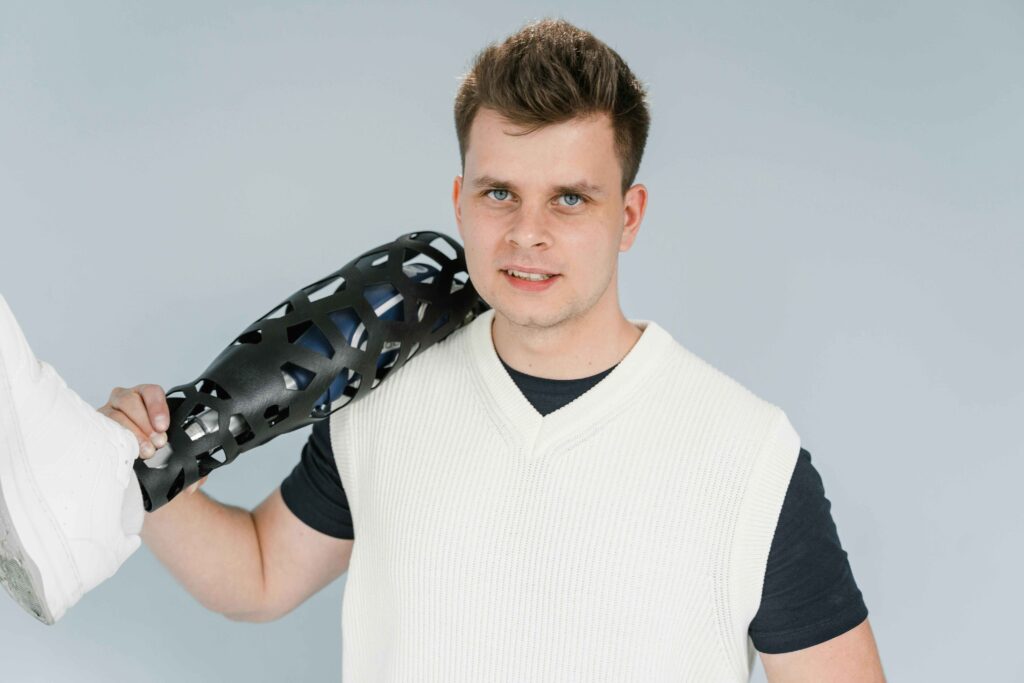

How 3D Printing Works in Prosthetics
This includes scanning of the residual limb or body part for the patient.
Prosthesis Design Customization: Depending on the anatomy and requirement of the patient, the design is done utilizing CAD software to customize the prosthetic.
Additive Manufacturing: Printing the prosthetic by layer on layer with materials like plastic, metal, or even biocompatible polymers.
Fit and Finishing: Assembled, tested, and fine-tuned for the comfort and workability of the user .
Advantages of 3D printed Prosthetics
1. Customization and Comfort
Orthotic prosthetics usually take very long periods fitting and do not fit a patient pretty close; however with 3D printing of prosthetics, it is possible to work on customization to come up with an item fitting a person’s limb perfectly with remarkable comfort and usability.
2. Cost
Prosthetics are quite expensive due to the rapid growth in young children, and therefore will change in relatively short periods.3D printing saves major cost production of making prosthetics available to the underserved population.
3. Rapid Production
Traditionally, prosthetics might take weeks or months to manufacture; however, 3D-printed prosthetics win on having a manufacturing time of mere days thus hastening recovery, and patients’ mobility.
4. Customization
In Form, Color, and Functionality Along designs, colors, and even the functional needs, patients can so decide so that their prosthetic reflects the choice and requirement of the patient himself or herself. The basic features like grip or attachment for all kinds of activities can be added very easily.
Impact of 3D-Printed Prosthetics on Healthcare
1. Inclusive Revolution
These prosthetics serve as a way for millions of amputees whose amputations cannot afford the cost and scarcity involved. This in the sense that these prosthetics can be made locally and at a cost-effective price almost everywhere using portable 3D printers.
The prosthetic limbs that the children require are very demanding in nature because they grow very fast. 3D-printed prosthetics have enabled easy replacement of prosthetic limbs at a cheap cost thus allowing the child to participate and be active.
3. Global Humanitarian Relief
3D-printed prosthetics, by products of non-profit organizations, have been used to make accessible and useful devices for underserved communities, including war-torn regions and developing nations.
4. Suitable Rehabilitation Programs
There shall also come a great outcome when advanced rehabilitation programs and a robotic limb or biofeedback systems are integrated with prosthetic innovation using 3D printing.
Obstacles in the Use of 3D-Printed Prosthetics
1. Material Obstacles
Where 3D printing boasts flexibility, strength and toughness of the materials which would have to be used for prosthetics is yet to improve enough to compare to other, conventionally produced devices best.
2. Legal Obstacles
Health care is one of the most strictly regulated areas in terms of patient safety. Lastly, 3D-printed prosthetics approval takes such a long time and is based on long procedures.
3. Skills Gaps
There are certain aspects of digital modeling, engineering, as well as health care skills that have to be enhanced through professional training education.
4. Servicing and Repairs
Because prosthetic devices 3D printed are not expensive, the most maintenance required is usually usually necessary, which in some cases cannot be possible in remote or developing regions.
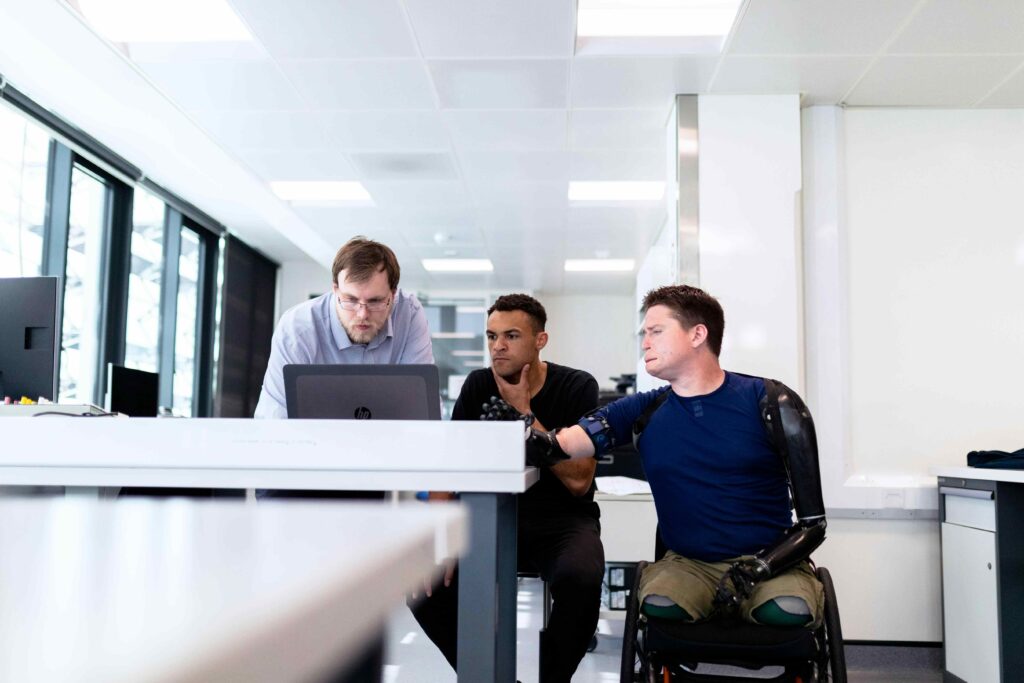

Technology Advancements in 3D Printed Prosthetics
1. Biocompatibility Materials
The development of biocompatibility materials has provided comfort and safety on utilizing 3D-printed prosthetics: providing a minimal response such as allergy or any form of reaction that might incur a slight discomfort.
2. Compatibility with Smart Technology
Prosthetics are being made intelligent through sensors, actuators, and IoT integration. These will give direct feedback, agility, as well as proper management of the prosthetic.
3. Bionic Limb
Bionic limbs will be one area of development in arms and legs through the emulation of natural functionalities of limbs by either robots or neural interfaces via 3D printing.
The prosthetics of the future can be designed modularly. That is to say that users might change and modify them without complete replacement.
Actual Life Application
1. Helping Victims of War
Lab helped win back their mobility, walk, and keep them as dignified as possible in countries such as Sudan.
2. Rehabilitation of Sportsmen
Such prospect of 3D printed prosthetics made the possibility to play at professional level in any sport real for amputees.
3. Changing Child Care
Speaking about the great creative feature of such technology, one can rather look at the example of a child named Jordan Reeves, who designed and has developed her own 3D-printed prosthetic arm with glitter cannon.
Prospects for 3D-Printed Prosthetics
Health is very relevant to technology, and 3D printed prosthetics are one of the fastest-emerging fields. Areas that can be followed closely include: AI-Powered Customization Artificial intelligence will provide a more specific design of prosthetics on obtaining information culled from scans from patients.
Global Partnerships Collaboration amongst governments, NGOs, and technological companies will make prosthetic limbs more accessible on earth at a relatively cheap cost.
Hybrid Production: The old ways blended with 3D printing will allow so much creativity but at the same time, much stronger and efficient prosthetic limbs.
Sustainability: This will be coupled with the uptake of environment-friendly materials that will have comprehensive recycling programs in the manufacture of 3D printed prosthetics.
This has proven to be quite promising in 3D-printed prosthetics and inspires innovation in all faces of health and relief operations. Other insights presented other ramifications and possible uses of the technology as educational and research opportunities.

Educational and Research Opportunities
Empowerment of Local Community: Most institutes and tech start-ups include 3D printing in curricula and workshops to empower local communities to conceptualize low-cost prosthetic limbs for its people.
Advancements in Medical Science: The universities and the research centers utilized 3D printing to check whether the new prosthetic limbs would indeed function as such, coupled with adaptive grip strength and sensory feedback mechanisms, etc.
Tech and Health Interface: The companies in the tech sector that collaborated with the health setups spearheaded the 3D printing prosthetic development opportunity through cross-pollination in knowledge from material science, robotics, and patient care.
Open Source Initiatives: The availability of free, open-source designs in blogs such as e-NABLE for the 3D printed prosthetics means there is an open source initiative meant to inspire participation all over the world to make low-cost solutions.
Social and Cultural Significance
Self-expression: This has been the new trend that the world is witnessing about 3D-printed prosthetics, where self-expression may occur with custom designs, patterns, or bright colors. Prosthetics can now be a combination of practicability and self-expression for a person.
Reducing Stigma: Aesthetic, attractive prosthetics are perceived as normal and reduce stigma usually associated with wearing an assistive device.
Economic Impact
Boost Local Economies: Since this process is readily available, small business and local entrepreneurship started to establish new units to manufacture prosthetics for all which in turn, provide employment and boost the economic growth.
Reduces Healthcare Costs: The cost-effectiveness in manufacturing brings very high reduction in cost of 3D-printed prosthetics, which reduces a significant burden on healthcare systems in resource-poor regions.
Extreme Environments: Researchers today are going to ask the questions of just how 3D printing materials can be used creating prosthetics that might be worn into extreme environments shortly, like underwater or even outer space.
Regenerative Prosthetics: Some of the research now is starting to look to combine regenerative medicine with 3D printing, possibly through bioprinting cartilage or embeeding stem cells into new generations of prosthetics.
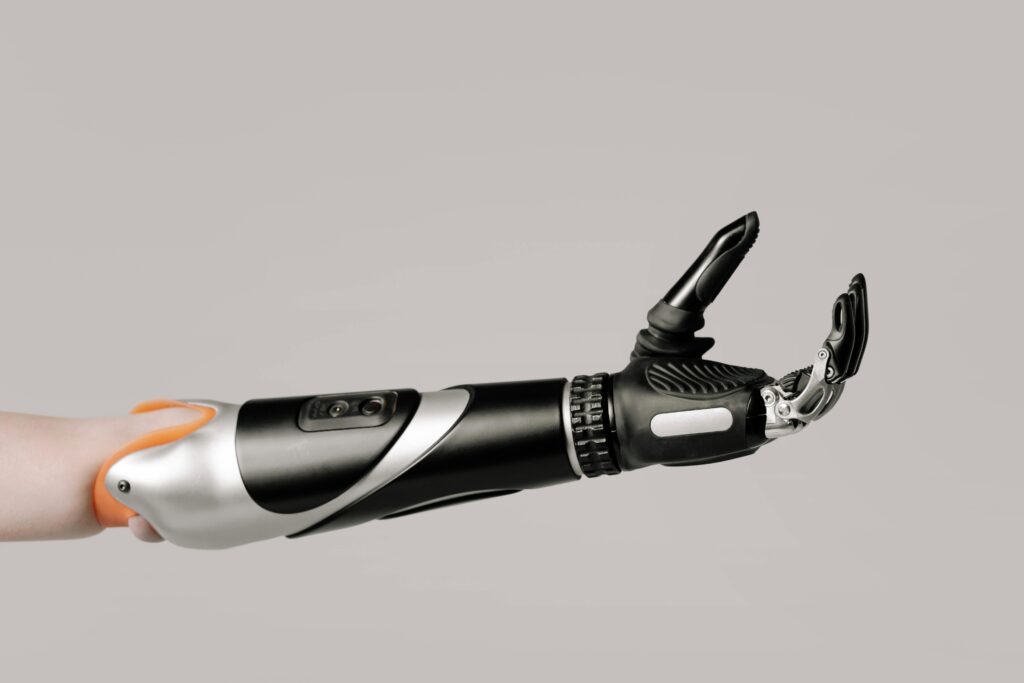

Call to Action: in Supporting the Movement
All our collective actions will dictate the future of 3D printed prosthetics. The big contributors will be the governments and the non-profits, even big businesses or little individuals who can all contribute in this revolution through;
Agitation for easier availability of affordable 3D printers for underprivileged regions.
Constant funding and research into new materials and advanced functionalities.
Spreading the word about this life-changing impact.
Conclusion:
3D-printed prosthetics are not only technological wonders but also a giant leap towards an inclusive, innovative, and patient-friendly healthcare delivery system. Customized affordable and accessible devices mean life is just transformed.The massive promises of possibly exciting possibilities with 3D-printed prosthetics seem to open up far greater possibilities as technology grows in the health sector, bringing mobility and rehabilitation possibilities that never seemed possible. Even the use of bionic integrations or sustainable practices seems to indicate that the future of custom-made healthcare solutions has never looked brighter.
Disclaimer:
Any information given out in the blog is for purely educational and informative purposes only. Though every precaution has been taken to make sure that everything contained herein is correct, no health or medical professional should take this article as professional medical advice and certainly not a recommendation to go out and see qualified health care providers. Decisions regarding any form of 3D printed prosthetics will depend on the person’s individual case and should be consulted with healthcare providers on a case-by-case basis. The authors and owners of the blogs included herein disclaim all liabilities for any decisions or actions undertaken based on the content provided herein.